1. 概要
Raft中的一个重要组件就是日志,另一个比较重要的是Raft节点传输的消息。
在etcd中,日志的实现是raftLog,消息的定义是Message。本文就看下这些组件的实现。
2. Raft日志
etcd-raft的Raft日志由raftLog实现,它里面有2个比较重要的数据结构和接口,它们分别是:
unstable结构:代表还没有持久化的数据Storage接口:提供了持久化日志的接口操作
2.1. unstable结构
unstable代表了还没有被持久化的数据,它包含2个部分:
snapshot:快照数据entries:日志数据(结构中记录了offset,则entries[i]的偏移量是i + offset)
这2部分同一时间只有1个字段非空:
- 当接收Leader的快照时,
snapshot非空 - 除了上面的情况外,
entries非空
2.2. Storage接口
Storage代表Raft日志底层存储模块,保存持久化的数据,它提供了持久化日志相关的接口操作:
InitialState() (pb.HardState, pb.ConfState, error):返回存储的初始状态,包括硬状态和集群配置Entries(lo, hi, maxSize uint64) ([]pb.Entry, error):传入日志索引范围和索引大小上限,返回符合这些条件的日志条目数组Term(i uint64) (uint64, error):传入日志索引,返回对应日志项的任期号LastIndex() (uint64, error):返回最后一条日志的索引FirstIndex() (uint64, error):返回第一条日志的索引Snapshot() (pb.Snapshot, error):返回最近的快照数据
2.3. MemoryStorage实现
不过在Storage接口的实现中,只找到了MemoryStorage,即内存实现,对外可作为cache使用。由于etcd-raft本身不实现存储,因此需要上层自己实现。
etcd本身的存储在
etcdserver/storage.go中定义和实现,接口也为Storage,其实现是带快照的WAL。在写入
raft的MemoryStorage前,会先写入WAL,详细细节超过了本文范畴。注意,不要把外部存储的
Storage和Raft的Storage混淆。
内存实现就非常简单了,只需要有下面的字段即可,对应的实现只需要赋值即可:
hardState:硬状态snapshot:快照数据ents:日志数据,其中ents[i].Index == snapshot.Metadata.Index + i,即快照数据和日志数据是相邻的
2.4. raftLog
etcd-raft日志实现位于raftLog结构中,使用了第2节所说的数据结构和接口,包括:
storage:Storage实例,保存已经持久化的日志、快照等数据,其中storage的实现是MemoryStorageunstable:unstable实例,保存还没有持久化的数据committed:当前已提交的日志项索引applied:当前上层应用已经应用到状态机的日志项索引,永远有applied <= committed
初始化时,raftLog设置完前2个参数后,设置committed和applied为firstIndex - 1,而firstIndex是storage中ents的第一项索引。初始化时raftLog实际上存储的布局类似如下:
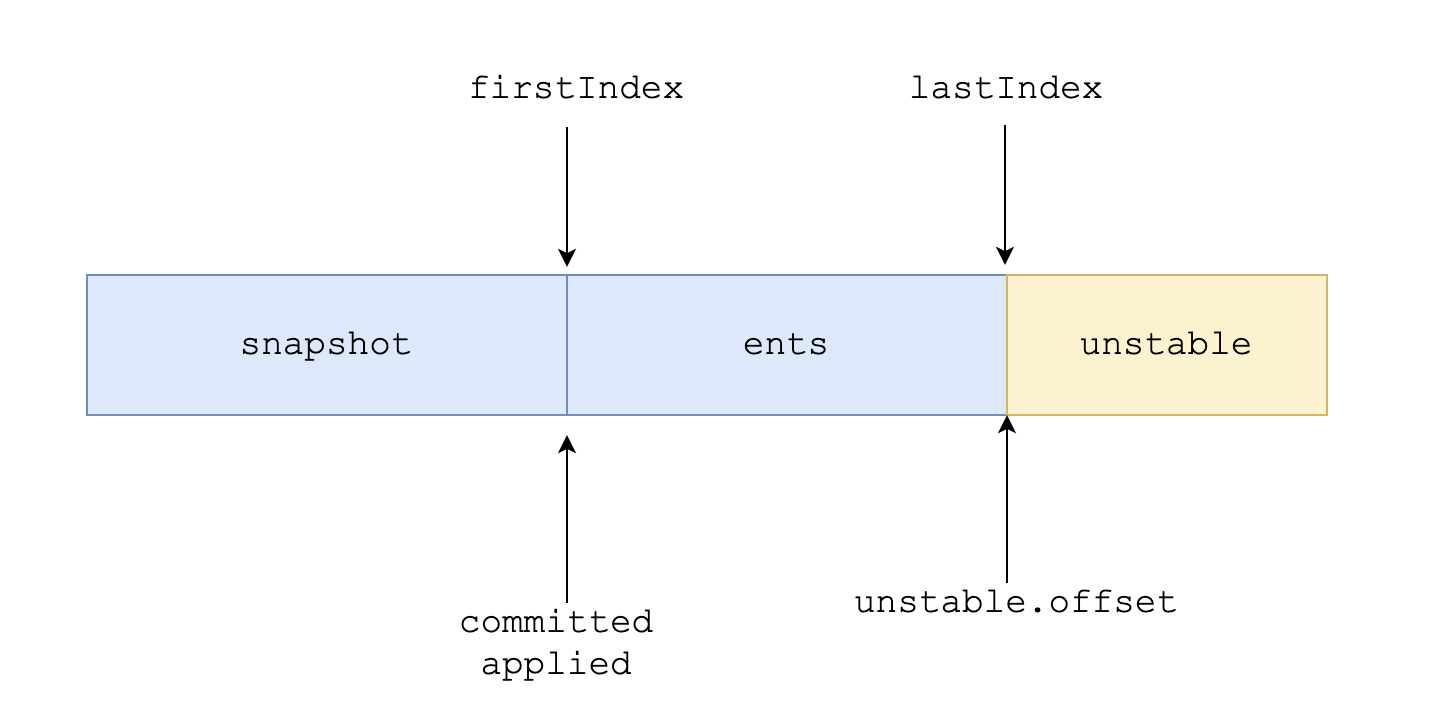
写入日志的时候,直接向unstable追加(可能需要截断旧日志)即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
func (l *raftLog) append(ents ...pb.Entry) uint64 {
if len(ents) == 0 {
return l.lastIndex()
}
if after := ents[0].Index - 1; after < l.committed {
l.logger.Panicf("after(%d) is out of range [committed(%d)]", after, l.committed)
}
// 直接向unstable追加
l.unstable.truncateAndAppend(ents)
return l.lastIndex()
}
提交日志的时候,只需要改动committed字段即可:
提交日志:
- 对于Leader:需要等到半数以上提交后才能提交
- 对于Follower:若请求不冲突,直接更新
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
func (l *raftLog) commitTo(tocommit uint64) {
// never decrease commit
if l.committed < tocommit {
if l.lastIndex() < tocommit {
l.logger.Panicf("tocommit(%d) is out of range [lastIndex(%d)]. Was the raft log corrupted, truncated, or lost?", tocommit, l.lastIndex())
}
l.committed = tocommit
}
}
而每次轮询Ready时,需要获取已经提交的日志项,这部分由nextEnts方法实现,它会返回applied + 1到committed的日志项数组切片(另外还会有大小限制):
若数组切片非空,则提交操作先于轮询操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
func (l *raftLog) nextEnts() (ents []pb.Entry) {
// 起始点为max(applied + 1, firstIndex)
off := max(l.applied+1, l.firstIndex())
if l.committed+1 > off {
// 结尾为committed, 返回日志切片
ents, err := l.slice(off, l.committed+1, l.maxNextEntsSize)
if err != nil {
l.logger.Panicf("unexpected error when getting unapplied entries (%v)", err)
}
return ents
}
return nil
}
轮询后,上层可把已提交的日志应用到状态机,之后就需要调用Node的Advance方法,它会更新applied索引,内部由appliedTo方法实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
func (l *raftLog) appliedTo(i uint64) {
if i == 0 {
return
}
if l.committed < i || i < l.applied {
l.logger.Panicf("applied(%d) is out of range [prevApplied(%d), committed(%d)]", i, l.applied, l.committed)
}
// 直接更新applied字段
l.applied = i
}
3. Raft消息
Raft协议中的消息种类比较多,主要分为选主、复制、快照等几类。etcd将所有种类的消息打包成一个数据结构Message:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
type Message struct {
Type MessageType // 消息类型
To uint64 // 接收者ID
From uint64 // 发送者ID
Term uint64 // 当前任期(term/epoch)
LogTerm uint64 // 日志所处的任期
Index uint64 // 日志索引,用于节点向Leader汇报自己已经提交的日志索引
Entries []Entry // 日志条目
Commit uint64 // 提交的日志索引
Snapshot Snapshot // 快照数据
Reject bool // 请求是否被拒绝
RejectHint uint64 // 拒绝同步日志请求时返回当前节点的日志索引,用于被拒绝方快速定位需要重新同步的日志项起始位置
Context []byte // 上下文数据
XXX_unrecognized []byte // 其他数据
}
而消息类型非常多,包含下面的类型,不同类型的消息会在之后说明etcd-raft功能具体实现时提及:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
const (
MsgHup MessageType = 0
MsgBeat MessageType = 1
MsgProp MessageType = 2
MsgApp MessageType = 3
MsgAppResp MessageType = 4
MsgVote MessageType = 5
MsgVoteResp MessageType = 6
MsgSnap MessageType = 7
MsgHeartbeat MessageType = 8
MsgHeartbeatResp MessageType = 9
MsgUnreachable MessageType = 10
MsgSnapStatus MessageType = 11
MsgCheckQuorum MessageType = 12
MsgTransferLeader MessageType = 13
MsgTimeoutNow MessageType = 14
MsgReadIndex MessageType = 15
MsgReadIndexResp MessageType = 16
MsgPreVote MessageType = 17
MsgPreVoteResp MessageType = 18
)
4. 总结
这里先看了一下etcd-raft所需要的重要数据结构,连同前文一起。之后会看下etcd-raft中关于选主、复制、快照、集群配置变化的功能实现。